Anna Waśkiel-Burnat, Michela Starace, Matilde Iorizzo, Alexandros Katoulis, Zoe Apalla, Leila Asfour, Azael Freites-Martinez, Dimitrios Ioannides, Seyed Morteza Seyed Jafari, Awatef Kelati, Francesca Pampaloni, Bianca Maria Piraccini, Adriana Rakowska, Andrea Sechi, Anita Takwale, Anastasia Therianou, Lidia Rudnicka
JEADV Volume 39, Issue 4, April 2025
Abstract
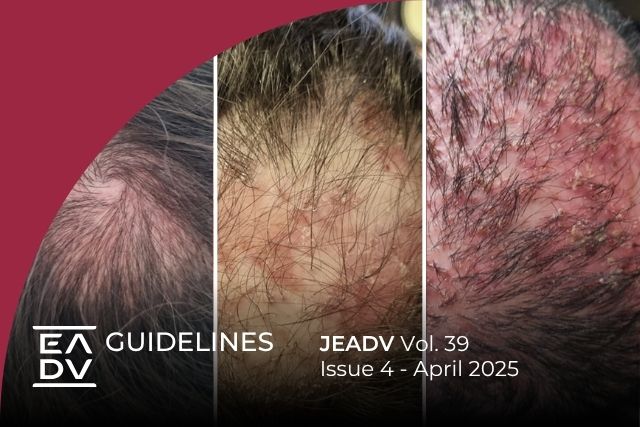
Folliculitis decalvans is the most common form of primary neutrophilic scarring alopecia, which is diagnosed in 2.8% of patients with hair loss. The course of the disease is typically chronic and relapsing. Thus, numerous therapies may be needed. Treatment extended beyond the resolution of the manifestations may be considered to avoid recurrences. As folliculitis decalvans is a form of scarring alopecia, the aim of any therapy is to control inflammation and prevent further hair loss. Hair regrowth cannot be expected. The aim of the EADV Task Force on Hair Diseases position statement was to propose diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for folliculitis decalvans. The therapeutic algorithm was created based on a literature review and clinical experience of the members of the EADV Task Force on Hair Diseases who are experts in hair disorders. In patients with folliculitis decalvans with moderate or severe inflammation, oral antibiotics should be recommended. In patients with highly active disease, a short course of oral glucocorticosteroids may be beneficial. Oral isotretinoin should be considered as the first-line therapy in patients with mild active disease (perifollicular erythema and hyperkeratosis, no pustules or crusts). Moreover, isotretinoin should be recommended in cases of refractory disease or persistent inflammatory lesions. Photodynamic therapy, biologics (preferably adalimumab), JAK inhibitors, oral dapsone, hydroxychloroquine or cyclosporine may also be effective. As an addition to systemic treatment, topical or intralesional corticosteroids should be recommended. Topical tacrolimus 0.1% or dapsone 5% may be considered as second-line topical therapeutic options. In patients with folliculitis decalvans, surgical excision or laser therapy can be useful. Hair transplantation can be considered in patients with inactive disease.


Log in to MyEADV with your EADV Membership account to get full access to JEADV