EADV Congress 2024
Session type: Updates
Room: Room 7.3
Date: Thursday, 26 Sep, 10:55 – 11:15 CEST
Part of Session: Hair disorders


Prof. Nino Lortkipanidze
(Tbilisi, Georgia)
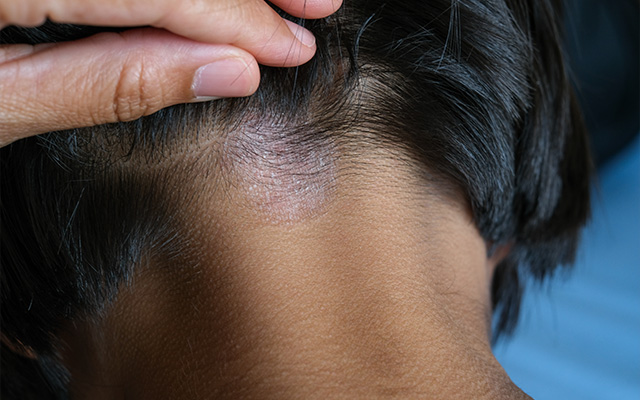
Several infections can affect the scalp and lead to various forms of hair loss (alopecia). These infections may affect the hair follicles directly or cause systemic changes that trigger hair loss.
The most common infectious causes of alopecia are:
- Fungal Infections:
- Tinea Capitis: This is a common fungal infection of the scalp. It leads to patchy hair loss with broken hairs and sometimes scarring alopecia.
- Bacterial Infections:
- Folliculitis: Bacterial infection of hair follicles, mostly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, which can lead to localized hair loss. Chronic folliculitis can lead to scarring and permanent hair loss.
- Syphilis: Secondary syphilis can cause patchy hair loss, known as “moth-eaten” alopecia, characterized by irregular patches of hair loss on the scalp.
- Viral Infections
- Herpes Zoster: When shingles affect the scalp, it can cause hair loss in the affected areas due to inflammation and scarring.
- COVID-19: has been associated with an increased incidence of telogen effluvium.
Also, the most common scalp disorders, such as eczema or psoriasis can be complicated by secondary bacterial infections. These infections can worsen inflammation and disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to hair thinning or patches of hair loss.
First and foremost, it is important to make a prompt and accurate diagnosis.
Trichoscopy, or scalp dermoscopy, is the best method for making differential diagnosis between scalp disorders as there are characteristic trichoscopy features in all diseases.